In this tutorial, we are going to discuss WordPress Settings. By default, WordPress comes with a few default settings set for you. You can override these settings to make WordPress work the way you want it to.
The settings are arranged in 6 logical groups:
- General Settings
- Writing Settings
- Reading Settings
- Discussion Settings
- Media Settings and
- Permalinks Settings
You can find all of these under the Settings menu on the left-hand side in your WordPress admin panel.
Let us discuss each of these settings in detail.
WordPress General Settings
As you can see in the below image, the General Settings page has quite a few fields that you can set.
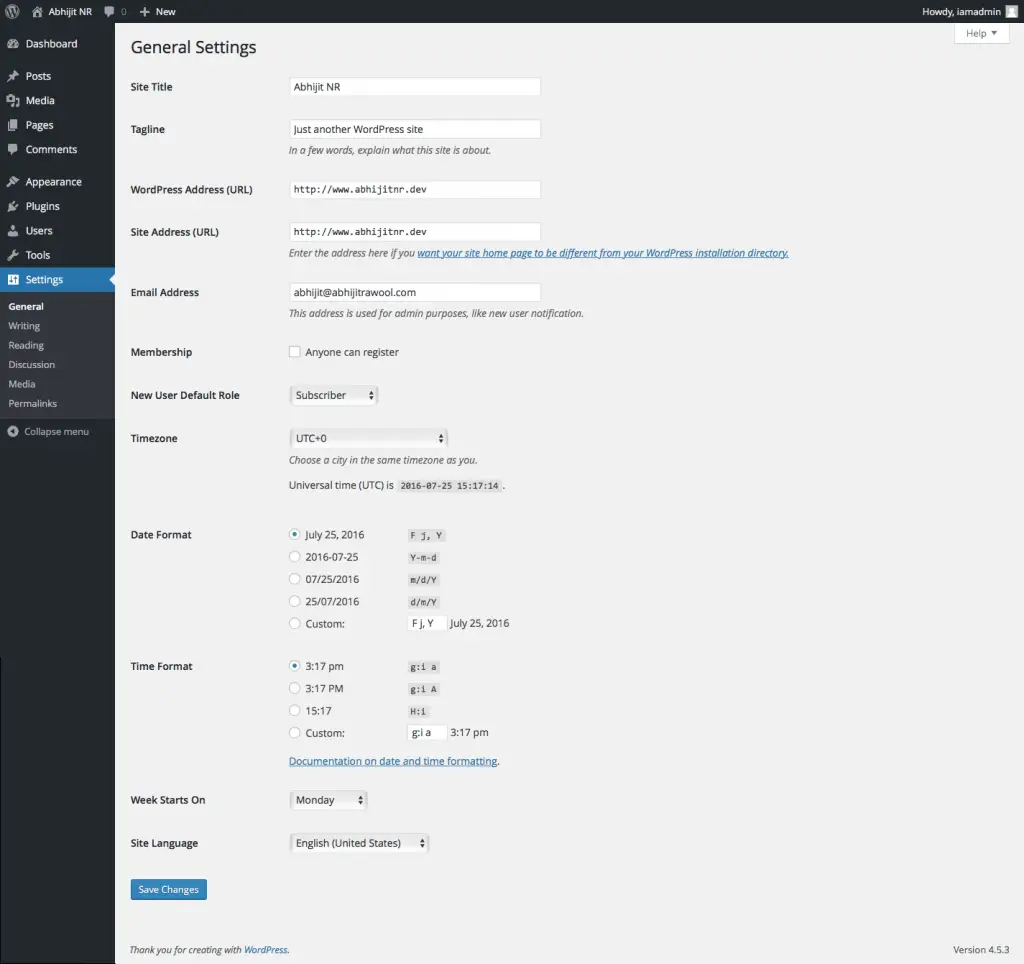
Site Title is the title or name of your site. And Tagline is the one line description of your site.
In most cases, WordPress URL and Site URL will be the same. However, you might want to set them differently in some cases. Read this article to understand when and how you may want to set these URLs differently – Giving WordPress Its Own Directory.
The Membership field indicates that anyone can register as a user on your site. By default this field is unchecked. The next field New User Default Role can be used to set the default role users will get when they register on your site. By default, the Role is set to Subscriber, and I recommend that you leave it as it is.
Rest of the fields are self-explanatory, so I will not cover them. Let us skip ahead to Writing Settings.
WordPress Writing Settings
The below image shows the fields on the Writing Settings page.
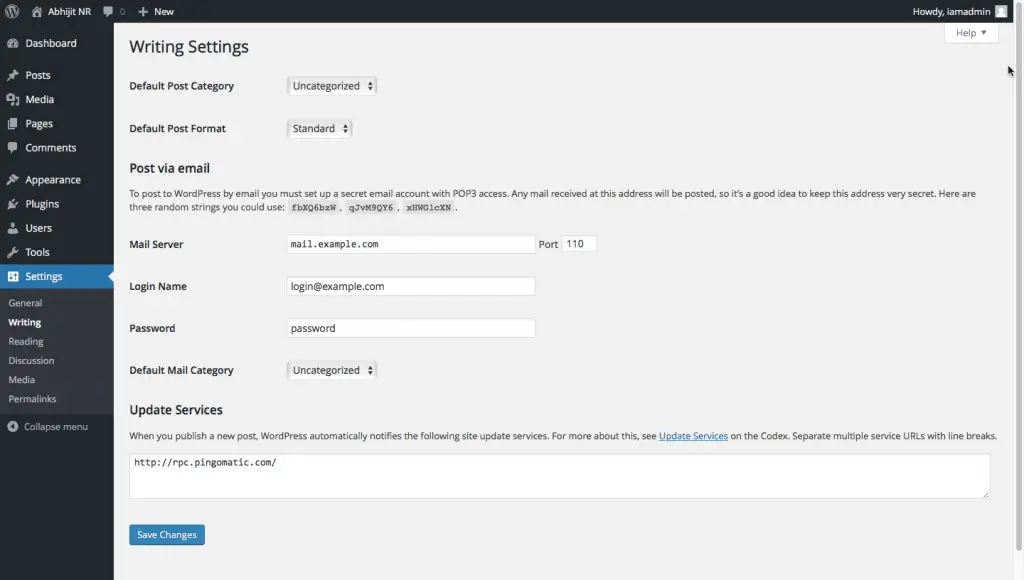
You can set the default Category that your Posts will get assigned to in the Default Post Category field. Keep in mind that whatever Category you select in this field cannot be deleted. You can read more about Categories in this tutorial – What are WordPress Categories? – The Ultimate Manual
The next field Default Post Format helps to set the default Post Format that your Post should be set to.
The “Post via email” section is an interesting one. It allows you to post to your WordPress blog by sending an email to a particular email address. You can read this detailed guide on WPBeginner on how to set this up: How to Add Posts by Email in WordPress.
The Update Service section can be used to specify the services that need to be automatically notified when you publish a new post. You can list multiple service URLs separated by line breaks.
WordPress Reading Settings
The Reading Settings page has the least number of settings as you can see in the below image.
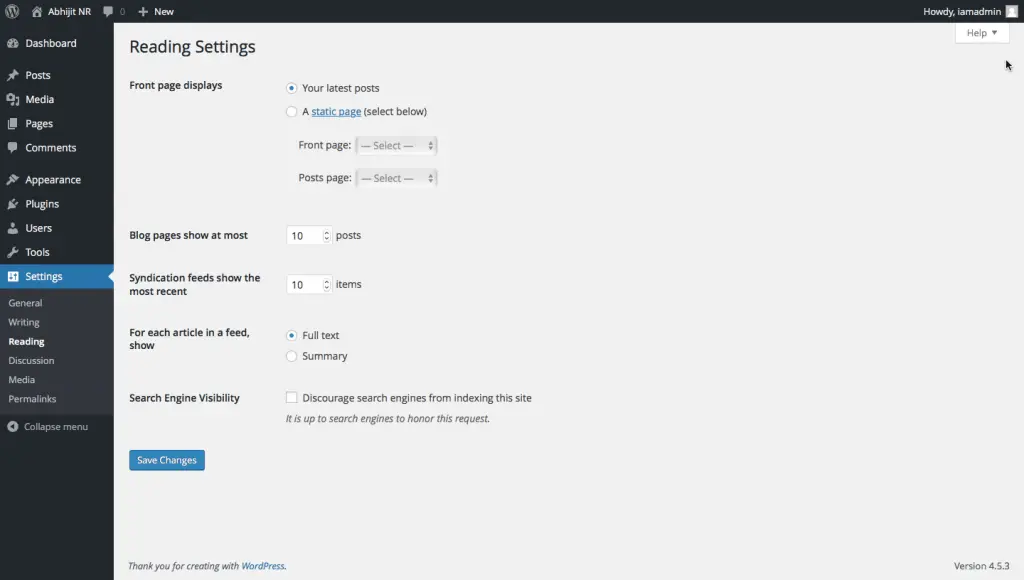
From this page, you can control which page is displayed as the home page of your site using the Front page displays field. By default WordPress sets your home page to display your latest Posts. Instead of that, you can set a different Page as your home page by selecting “A static page” option and then by selecting the Page in the Front page field that you want to display as the home page. You can then set the page that will display your blog posts in the Posts page field.
You can also set the number of blog posts that you want to show to your site’s visitors on the blog page. You can also set the number of items to be displayed in the RSS feed as well as whether they need to be displayed in full or just their summary.
Lastly, you can also control whether or not the Search Engines should be able to index your site using the Search Engine Visibility field. This is especially helpful when you are building your site and don’t want the pages to show up in search engines. Don’t forget to uncheck this setting once you are ready to launch your site to the world.
WordPress Discussion Settings
These settings help you to deal with the comments that you receive on your Posts.
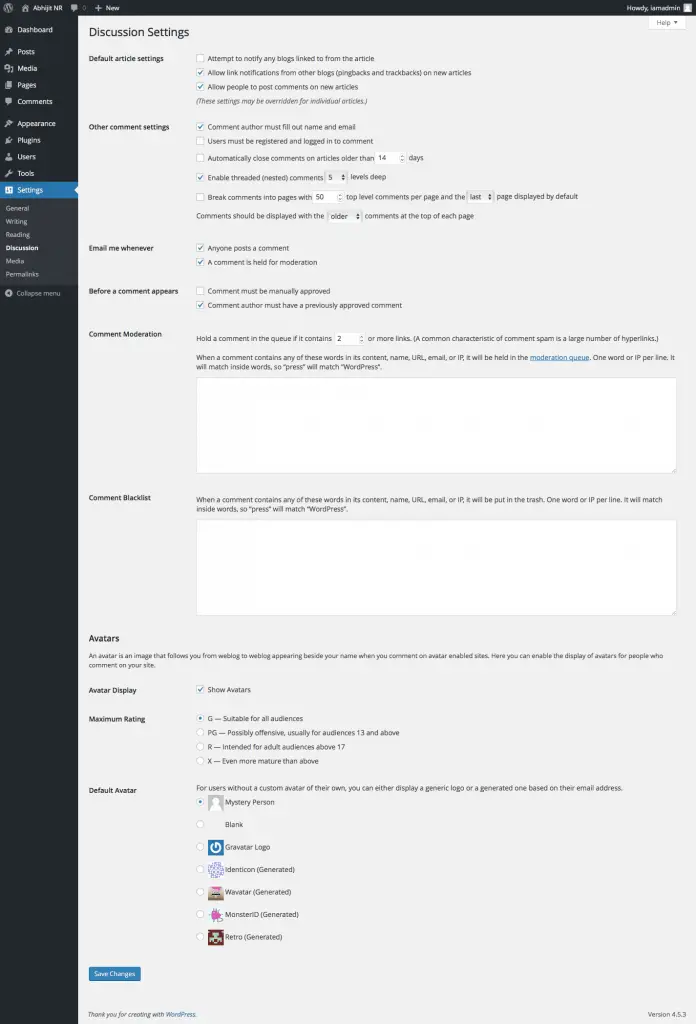
You can see in the above image that there are a number of settings that you can set. Most of these settings are self-explanatory. So I will not discuss each one of them.
I have found that mostly the default Discussion Settings are good enough for me. But you can change them if you want to.
WordPress Media Settings
Media Settings are used to set the sizes your images will be converted to after you upload them to your site.
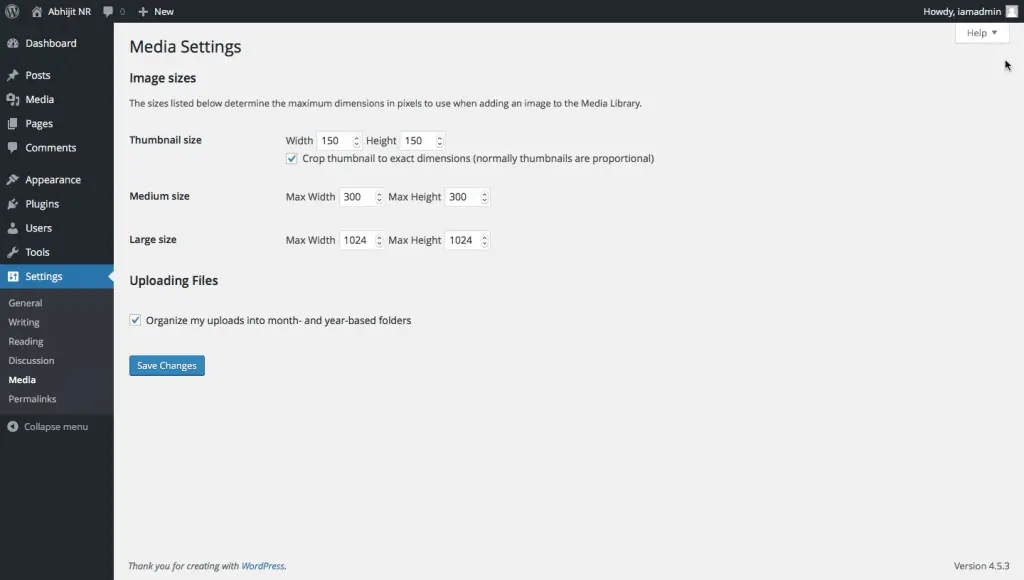
For every image that you upload, WordPress will generate images of the sizes that you specify in the “Image sizes” section. It will then store and organize those images in the month and year based folder format if you have checked the option under “Uploading Files” section.
WordPress Permalink Settings
These settings are probably the most important settings because these dictate how the URLs of your site will look like.
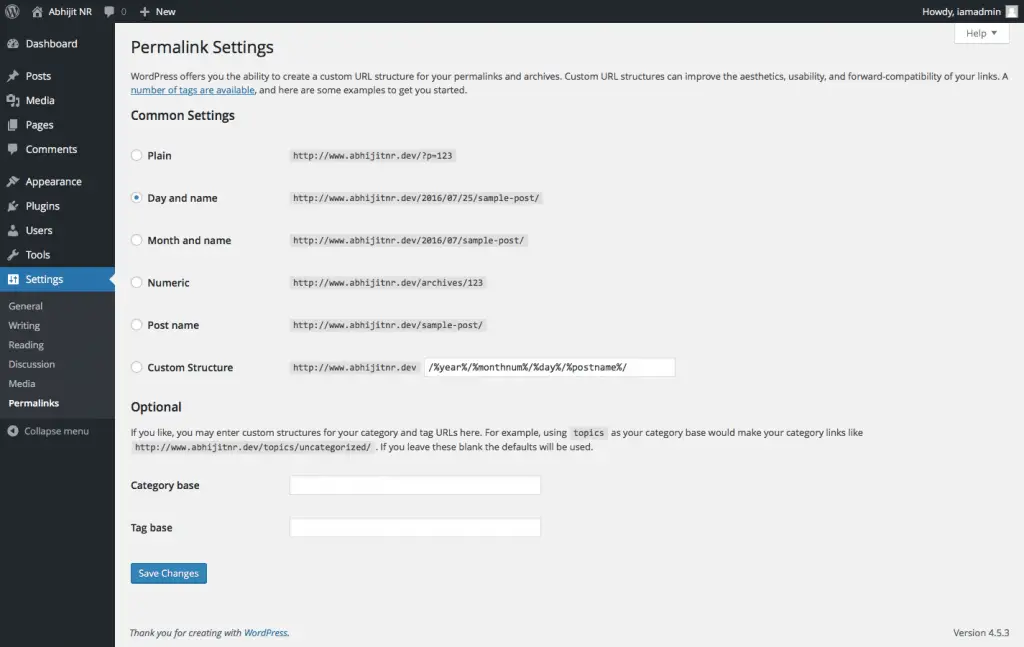
As you can see under the “Common Settings” section, there are a lot of different ways in which you can structure the URLs. There has been a lot of debate on which one of these is a good URL structure for SEO (Search Engine Optimization). Do a Google search and you will find plenty of articles that are trying to answer this question.
If you too are in a dilemma then “Post name” is a good choice to start with. I have been using this format on all of my sites and I have not seen any negative impact on SEO because of using this format.
You can even set a custom URL using Structure Tags. You can read more about them on the official WordPress Codex – Using Permalinks.
The Category base and Tag base fields under Optional section help to define the URL structure for the Category and Tag pages. For example, if you have a Category called “WordPress” then by default the URL for the Category page will be – http://example.com/category/wordpress. Now if you set the Category base field to “cat” then this URL will change to http://example.com/cat/WordPress. Similarly, you can change the URL of Tag pages using the Tag base field.
End of Settings!
That ends this tutorial.
I hope you have got a good understanding of the various WordPress Settings available to you and which ones you can tweak to make WordPress function the way you want it to. If you want to learn more about making WordPress websites, then read this detailed tutorial on how to create a WordPress website.
If this tutorial helped you then please do share it with your friends. I will really appreciate that.